|
Magna
Grecia
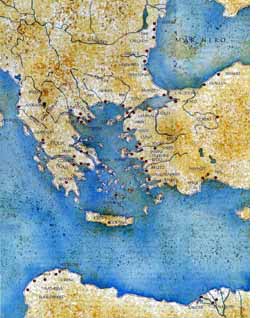
The
term "Magna Grecia" is used to describe the area occupied by Greek colonization
outside of the immediate area of the Aegean Sea (in the center of the
map on the left). This wave of colonization started in the 8th century
bc. It took the idea of the polis --the independent Greek city-state
-- a bit to the east into the Black Sea, down along the coast of Africa,
and, particularly to the Italian peninsula, where thriving and independent
Greek city-states flourished on Sicily and much of the southern half of
the peninsula (see map, below. Each red dot on the maps is the site of
a prominent Greek settlement).
(continued below)
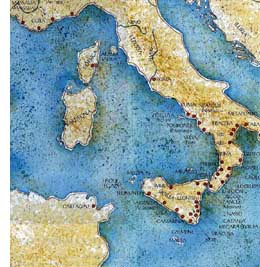
The
map on the right shows the extensive network of Greek cities in southern
Italy during the age of Magna Grecia. The first settlement was on the
island of Ischia. That settlement then moved across to the mainland and
founded Cuma. To read an article about Greek presence in the gulf even
before Magna Grecia, read Uncovering the Bronze
Age on Procida. You may also read "Ancient Peoples of Italy" (click here), dealing with some of the early indigenous
peoples of the peninsula, many of whom were absorbed by Greek colonization.
Magna
Grecia in Italy, of course, came to an end as Rome, itself, expanded into
empire. Of all the Greek sites represented by the red dots, only Naples
has survived as a continuously inhabited center of large population.
back to main map list
back to encyclopedia index
back to Around Naples English main
page
back to home page of napoli.com
|
